1. What is a photovoltaic inverter:
Photovoltaic inverters can convert the variable DC voltage generated by photovoltaic solar panels into mains frequency AC inverters, which can be fed back to the commercial transmission system or used for off-grid grids. The photovoltaic inverter is one of the important system balances in the photovoltaic array system, and it can be used with general AC power supply equipment. Solar inverters have special functions for photovoltaic arrays, such as maximum power point tracking and island effect protection.
Grid-connected inverter classification:
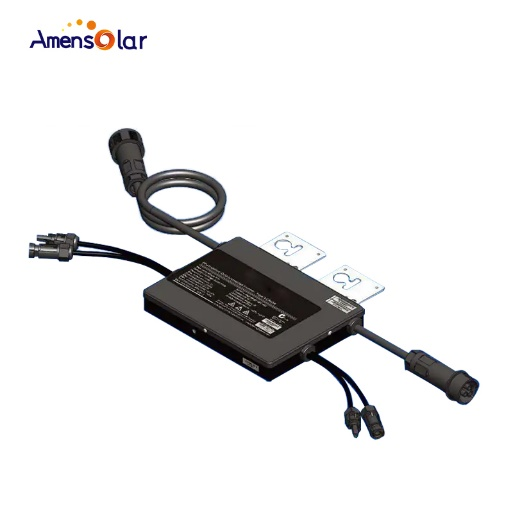

1. Micro inverter
A solar photovoltaic microinverter is a device that converts direct current from a single solar cell module to alternating current. The DC power conversion of the micro-inverter is AC from a single solar module. Each solar cell module is equipped with an inverter and a converter function. Each component can perform current conversion independently, so this is called "micro-inverter device".
Microinverters can achieve maximum power point tracking (MPPT) at the panel level, which has advantages over central inverters. In this way, the output power of each module can be optimized to maximize the overall output power.
Each solar panel is connected to a micro-inverter. When one of the solar panels does not work well, only this one will be affected, while the other photovoltaic panels will operate in the best working condition, making the overall system Higher efficiency and greater power generation. In addition, in combination with the communication function, it can also be used to monitor the status of each module and detect a failed module.

A hybrid inverter can perform both functions of inverter and energy storage at the same time. A hybrid grid-tied inverter can convert DC to AC to power your home, but it can also take AC from the grid and convert it to DC to store in energy storage for later use.
If you are adding battery backup to your system, choose a hybrid inverter for maximum design flexibility, enhanced monitoring capabilities, and reduced overall maintenance.
Currently, hybrid inverters have higher upfront costs than traditional grid-tied inverters. In the long run, you can save more money than buying a non-hybrid inverter and a battery backup inverter separately.
How to choose the right solar inverter for your system?

| Type |
Grid-Tie Micro Inverters |
Hybrid Inverters |
| Economical |
Reasonably priced |
Reasonably priced |
| Single Point Of Failure |
No |
Yes |
| Expandable? |
Easier to expand |
Yes but not easily |
| Performs Well in Limited Shade? |
Yes |
Limited shade tolerance |
| Recommended For Roof or Ground Mounted System? |
✓ Ground mounted |
✓ Ground mounted |
|
✓ Roof mounted |
||
| Can I Monitor Each Solar Panel? |
Yes, panel level monitoring |
System level monitoring |
| Can I Add a Battery in the Future? |
Yes, but difficult |
Easy battery expansion |
| Can I Add a Generator? |
Yes, but difficult |
Easy to add generator |
Post time: Apr-03-2024